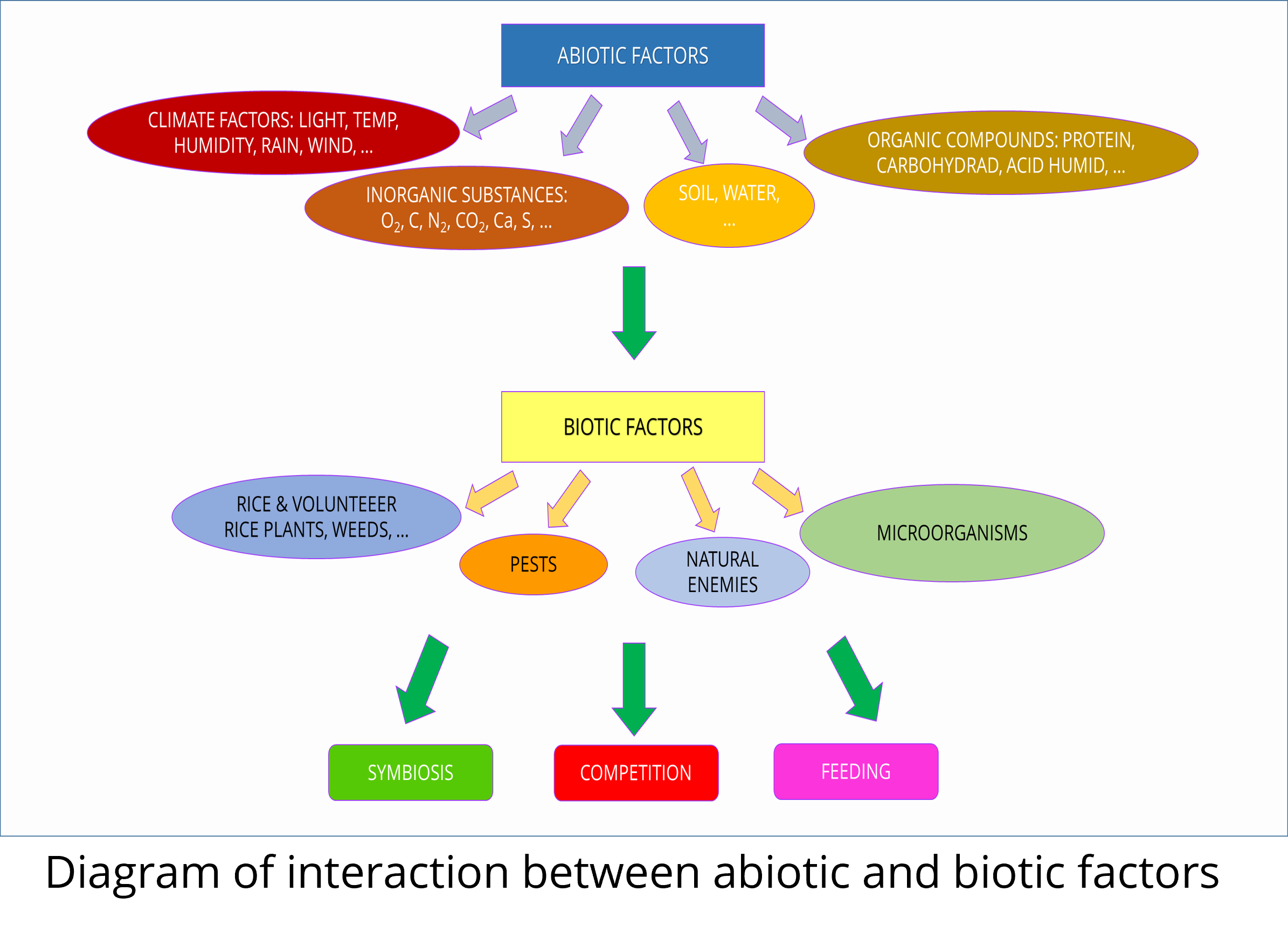
ABIOTIC FACTORS:
- Are necessary elements for development of rice crop and change from time to time (year, month, season …) and space (different ecological zones ….) and impact on biotic factors such as growth of rice plants, outbreak of pests and diseases, ….
- Different living organisms need different abiotic factors to survive. Different living organisms have different levels of tolerance for different abiotic factors.
- Even decide which organisms will survive in an ecosystem and how many of them will be able to continue to live there.
Types of interaction among biotic factors:
- Competitive relationship: is the competition between two or more species for food, living space…as a result, this species will destroy other species. In rice field ecosystem, rice plants compete with weeds for nutrition, soil, water, light …So if weeds are growing well, then vigor of rice plants reduced.
- Symbiotic relationship: in the rice field ecosystem, there are symbiotic cyanobacteria living with water hyacinth (Azollaceae) to fix nitrogen needed for rice crop.
- Host plant relationships: the interactions between species living on host organisms can harm and kill the host (fungi, bacteria harmful to rice).
- Predator/parasitoid-insect pest relationships: There are two main contributing factors in the rice ecosystem, which are biotic factors as rice plants, insects, microorganisms, and other animals… and non-living/abiotic factors including soil, water, light, temperature, humidity, rain, organic matter and inorganic substances…. and they interact together to form natural ecosystem.
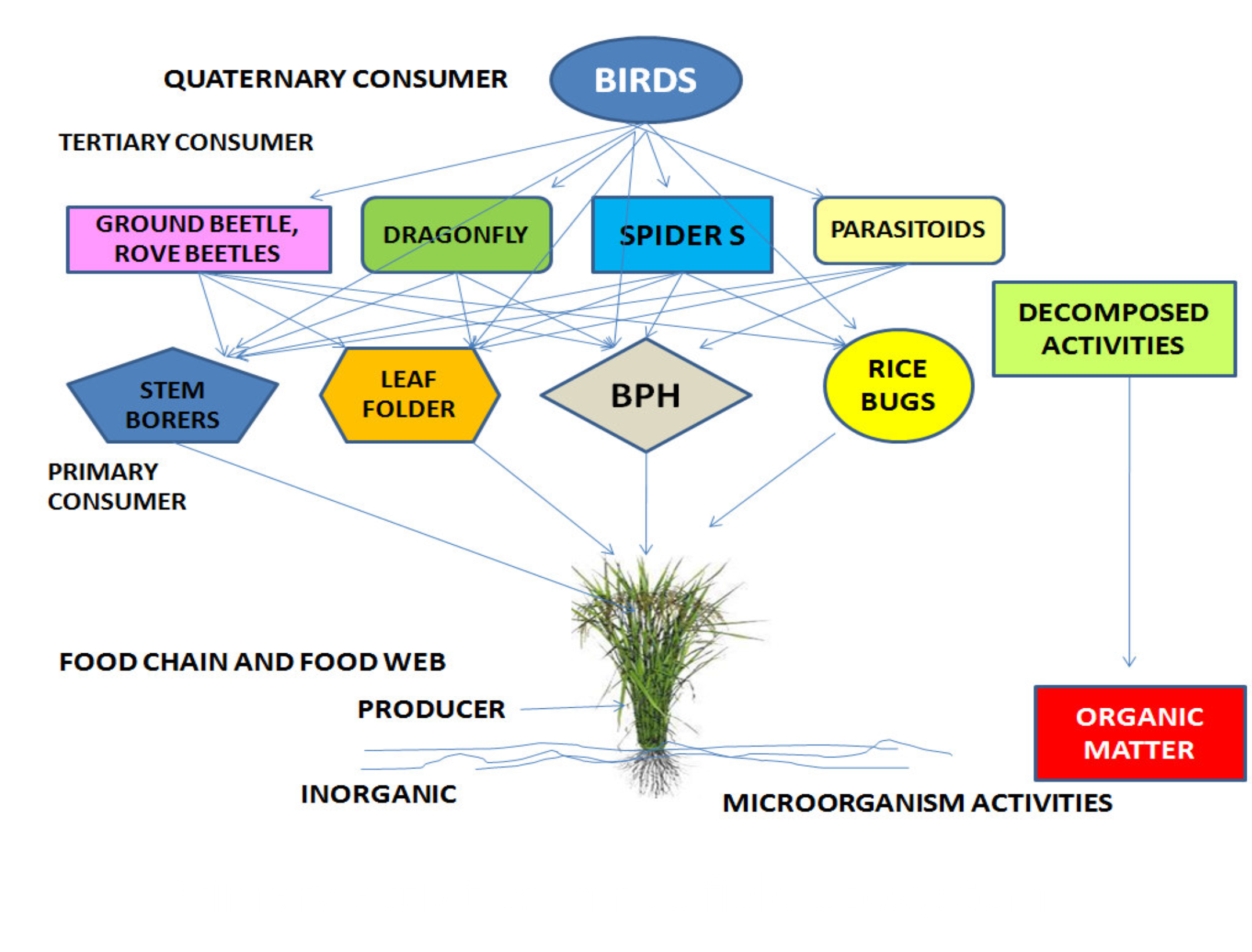
- In the rice field ecosystem, there are a lot of insect pests that occur in all the stages of rice crop including weeds, insect pests, diseases, rats and snails. Naturally, the relationship between rice plants- pests –natural enemies balances in the rice ecosystem because natural enemies may control the population of the insect pests below the damage level by preying or parasite on their hosts (ex: Lycosa spiders, wolf spider, Rove beetles, ground beetle….or parasitoids) that prevent a pest outbreak.
- In generally, the contribution of natural enemies in Integrated Pest Management is very significant in making biodiversity of the rice field ecosystem. This relationship between predators, parasitoids and insect pests is very important. In nature, predators/parasitoids always tend to limit insect pests to make ecological balance. Therefore, they must be protected by applying ecological engineering and reducing the number of times of insecticide application, using selective and preferably biological insecticides.
Course Outline
Course Outline
