Management will influence the time and uniformity of crop maturity. The basic requirements of good crop management include:

1. Plant technique and population
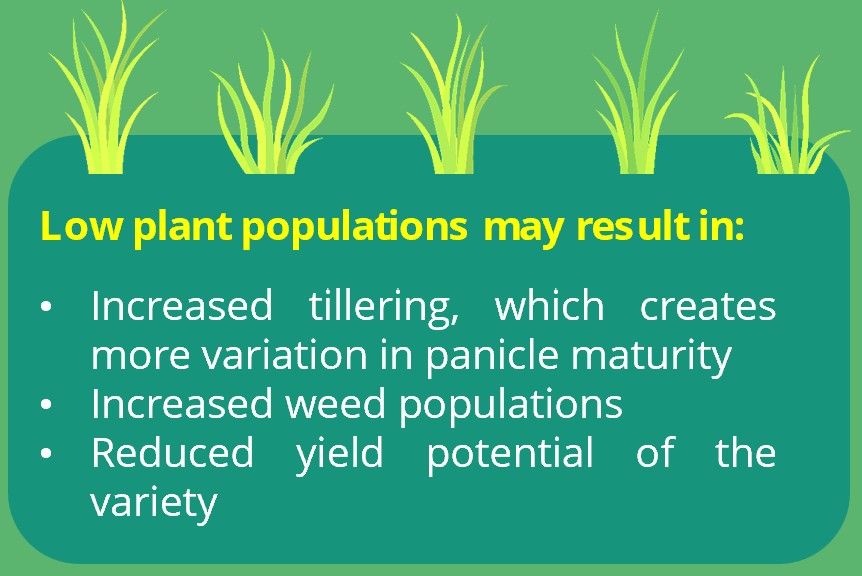
Establishing the correct number of plants is essential to maximize water and nutrient use. A target population that results in 400–500 panicles/m2 is desirable.

This means establishing at least 70–100 seedlings/m2 when transplanting or broadcasting 80–120 kg seed/ha when direct seeding. When a high-value seed is used, single seedlings are planted on each hill.

2. Seed dormancy
Many rice varieties have a dormancy period immediately after harvest. This usually lasts up to 1 month during which time germination levels are low and variable. A number of different
treatments are used both to break dormancy and improve seed establishment.

3. Water management
To be able to manage water, the fields must be level and the bunds or levees well maintained.

Uniform water depth across the field will contribute to more uniform crop, higher seed yields, and consistent MC in the grain sample. Reducing the variation in MC at harvest reduces the chance of seed damage from diseases.

4. Nutrient management
The application of the correct level and type of fertilizer for the variety and growing conditions is essential. The prudent application of N is essential to get an even maturing crop with full grain size.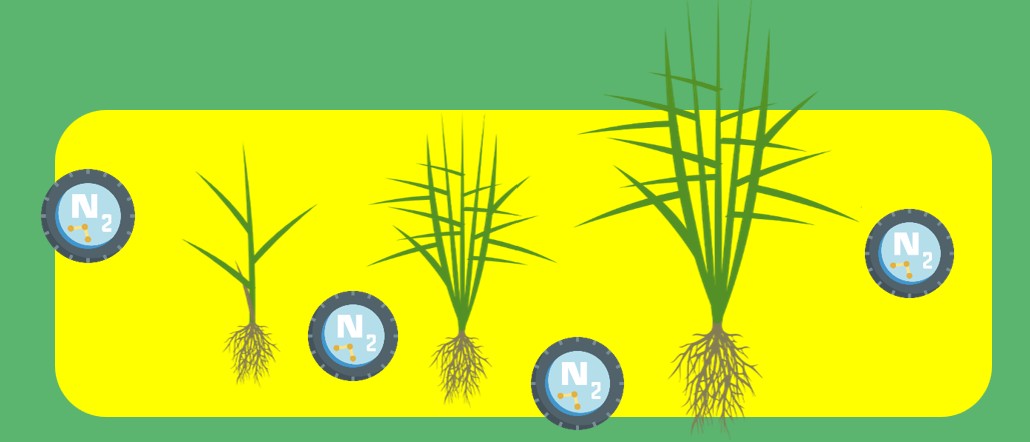

5. Roguing
Every field should be rogued to remove off-types, any plants of another crop, late-maturing weeds, other varieties, and diseased plants.

Roguing should be done at least once before flowering and once after flowering and may reduce potential crop yields up to 10–20%.
Characteristics that can be used to determine varietal purity under field conditions include:
- plant height
- pigmentation of plant parts
- pubescence
- panicle characteristics
- time of flowering
6. Harvest management
The higher the quality of the seed, the greater the care that is required in harvesting and threshing the seed. Seed harvest should require specific harvesting systems and machines (e.g., threshers and combine harvesters).

